SLELO PRISM- Rob Williams
Invasive species affect almost all aspects of our culture. They interfere with many types of outdoor recreation. They reduce crop yields and interfere with harvest operations on local farms. Along public roads and highways, invasive plants restrict visibility and create roadside hazards. Invasive insects and diseases kill trees in forested areas, as well as along community streets. Some invasive species even have a direct negative impact on public health.
In 2004, some sixteen years ago, the economic impact of invasive species in the United States had been estimated at 120 billion annually, (Pimentel, et. al.2004). Add sixteen years of an average inflation rate of 0.9% modestly, and impact would be 163 billion annually (Bureau of Labor Statistics 2020) Pause for just a moment and let that resonate 163 billion! Local and regional communities have been challenged with preventing and controlling invasive species or remediating their impacts at costs ranging from several thousand to millions of dollars. This economic impact affects local, regional and state budgets directly through prevention and management costs; indirect costs are endured when the value is placed on things like recreation which can be suppressed by poor water quality or reduced access issues due to the presence of invasive plants—real estate values and resale can be lessoned by the same.
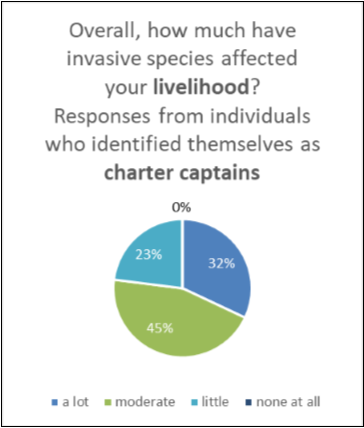
A Cultural Impact Study completed by the SLELO PRISM in 2016, suggests that, in addition to the ecological and economic impacts of invasive species, these same species have an effect on the well-being and livelihoods of people locally and regionally (Williams, R. and T. Ives 2016).
Economic, cultural, and ecosystem impacts resulting from invasive species invasions, signify the need for continued prevention and management. By addressing the threat of invasive species, PRISMs and other community partnerships can have tangible and lasting effects in the mitigation of the negative implications caused by invasive species. These actions, in-turn will stimulate tourism, water, and land-based recreation, travel, and will play an important role in the social well-being, and recovery of local, regional, and statewide economies.
Click to read the full summer 2020 E-newsletter